Health
Morning Workouts vs Evening Workouts — Which is Better For Your Health?
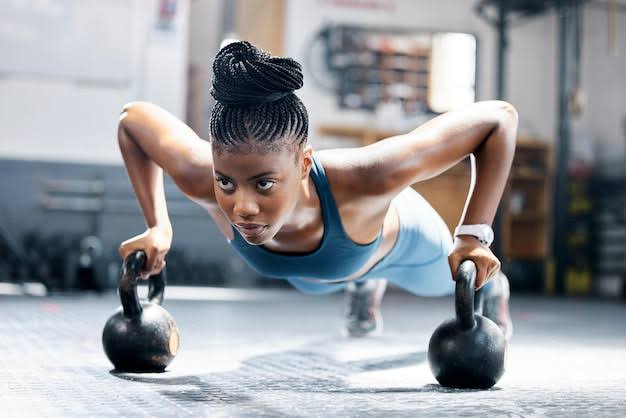

We all want to stay fit and healthy. But one common question that often comes to mind is: Should I work out in the morning or in the evening? Some people enjoy waking up early and starting their day with a workout. Others feel stronger and more energized in the evening. So, which option is healthier? Let’s find out.
The Benefits of Morning Workouts
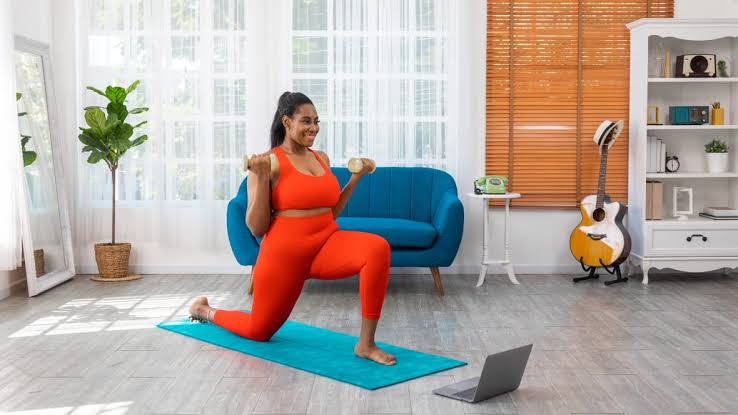

Some people prefer exercising in the morning. Morning workouts help wake you up and energize you for the day. When you exercise, your body releases endorphins—feel-good chemicals that relax you and reduce stress. These help keep you calm and focused throughout the day.
Exercising in the morning also helps you stay consistent. It allows you to complete your workout before daily responsibilities, like work or errands, get in the way. Some studies even suggest that morning workouts help regulate appetite and improve sleep at night.
For those trying to lose weight, exercising in the morning before eating may help the body burn fat more efficiently. However, this benefit can vary depending on your body type and specific fitness goals.
The Benefits of Evening Workouts
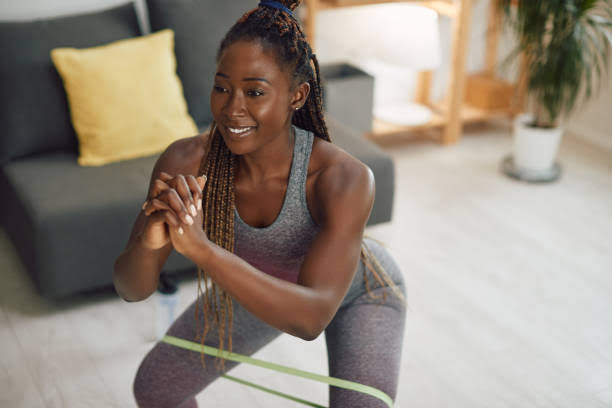

Not everyone likes to exercise early in the morning. Many prefer evening workouts due to their work or school schedules. After a busy day, exercising can help reduce stress and tension, making it a great way to unwind before bed.
Your body temperature is also higher in the evening, which makes your muscles more flexible and reduces the risk of injury. This means you may perform better—lifting heavier weights or running faster—than you would in the morning. Having eaten throughout the day also gives your body more fuel for a stronger workout.
Evening workouts can also be social. Whether it’s a group class, gym session with friends, or a post-dinner walk with family, evening exercise can be fun and motivating.
Which is Better?
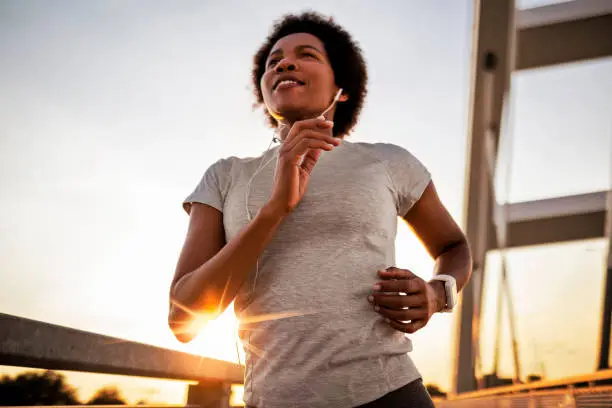

The truth is, both morning and evening workouts offer great benefits. What matters most is choosing a time that fits your lifestyle. If you enjoy working out in the morning and it fits your schedule, then stick with that. But if you feel more energized and relaxed in the evening, that’s perfectly fine too.
The key is consistency. Regular exercise—whether in the early hours or later at night—is what keeps you healthy and fit. Whether you’re running at dawn or hitting the gym after dark, both can help you reach your fitness goals.
There’s no universally right or wrong time to exercise. Both morning and evening workouts can boost your health and happiness. The best workout is the one you enjoy and can stick with. Listen to your body, choose a time that works for you, and take full advantage of all the benefits that exercise offers.
Health
Workout Routines That Support Bones Health

Strong bones depend on more than just calcium or supplements. Research shows that bones respond to physical stress: when muscles and weight-bearing activities challenge the skeleton, bone tissue becomes denser and stronger. To protect skeletal health over the long term, exercise should combine weight-bearing activity, resistance training, and balance work. Together, these exercises address the main risk factors for fractures: low bone density, weak muscles, and poor coordination.
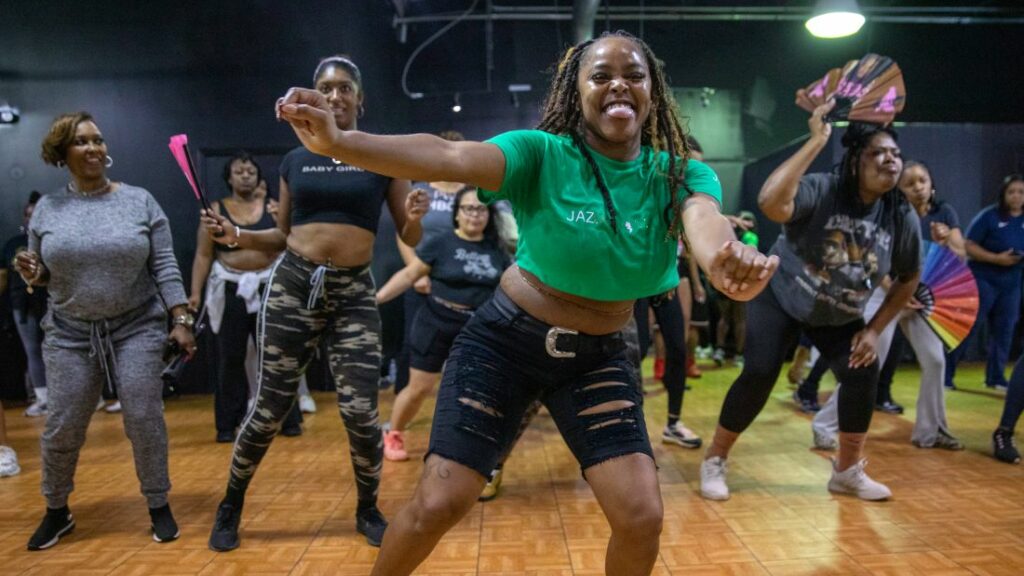
Photo Credit – Google
Weight-bearing activity doesn’t need to be extreme to be effective. Regular brisk walking around neighbourhoods or local parks strengthens hips, legs, and spine, while climbing stairs or light jogging improves lower-body density. Dance classes, including Afrobeat or traditional Nigerian dances, provide varied movement patterns that engage muscles and improve coordination. Starting with 15–20 minutes per session, three to five days a week, and gradually increasing intensity or duration can deliver measurable benefits.

Photo Credit – Google
Resistance training plays a key role in maintaining strong bones. Gradually increasing weight or resistance helps muscles and bones adapt. Exercises such as squats and deadlifts target the hips, thighs, and spine, while lunges and step-ups build strength in the lower body and promote functional movement. Push-ups, pull-ups, and shoulder presses strengthen the upper body and spine. Two to three sessions per week covering all major muscle groups are sufficient. Free weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises can all be effective depending on what equipment is available.

Photo Credit – Google
Balance is equally important because falls are a leading cause of fractures. Single-leg stands and heel-to-toe walking improve stability and coordination, while yoga, Tai Chi, or mobility exercises enhance control and complement other workouts. Integrating balance with strength and weight-bearing exercises provides a complete approach to bone health.
Common mistakes include relying solely on low-impact cardio such as swimming or cycling, which has little effect on bone density, and attempting high-impact exercises without preparation, which can increase injury risk. Effective routines should be planned, progressive, and performed consistently to build resilience safely.
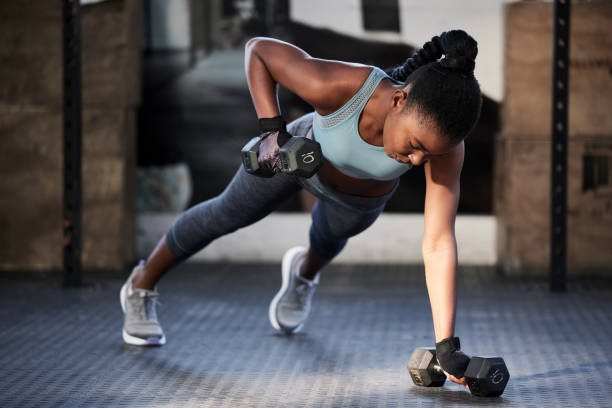

Photo Credit – Google
A sample weekly schedule could include strength-focused exercises on Monday, such as squats or step-ups, deadlifts or hip-hinge movements, and push-ups or shoulder presses. Wednesday could focus on weight-bearing activity and balance through brisk walks, single-leg and heel-to-toe drills, and light dynamic movements. Friday can target functional strength with lunges or carries using household objects, core stability exercises, and stretching or yoga. This cycle can be repeated weekly, increasing load or complexity gradually.
Strong bones require intentional, evidence-based exercise. By combining weight-bearing activity, resistance training, and balance work, Nigerians can maintain bone density, reduce fracture risk, and improve overall skeletal resilience. Starting at your current fitness level, increasing load progressively, and including balance exercises will help protect bones for the long term.
Health
Disordered Eating Vs. Eating Disorder: Experts Explain The Differences And When To Seek Help
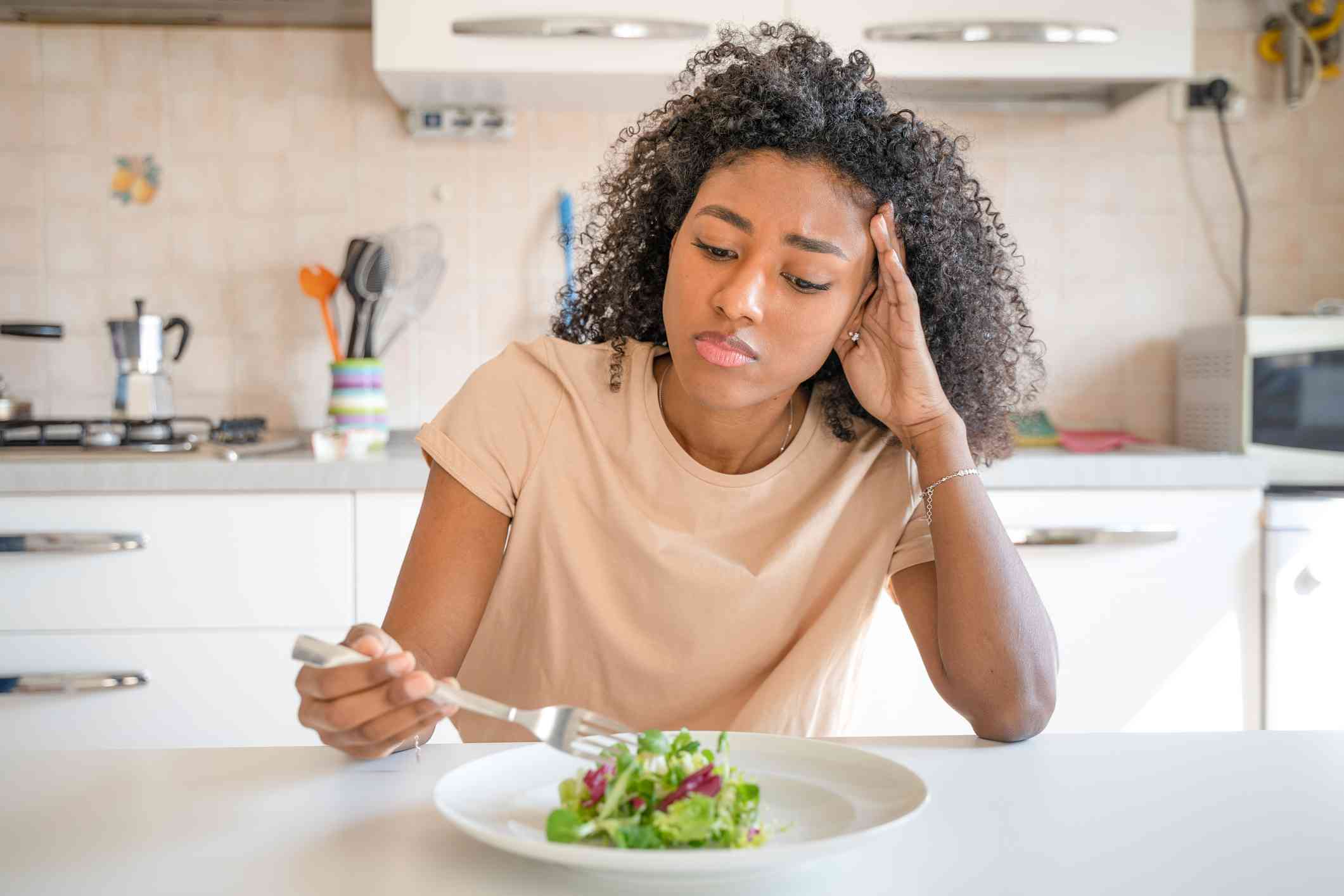

Disordered eating and clinical eating disorders are not interchangeable. Disordered eating refers to irregular or emotionally influenced habits around food: chronic dieting, skipping meals, rigid food rules, occasional binge episodes or persistent preoccupation with calories, weight or body shape. These habits may shift, but when repeated over time they often point to growing vulnerability.
Clinical eating disorders, by contrast, are diagnosed mental-health or medical conditions marked by persistent, patterned behaviours that impair physical health, mental wellbeing or daily functioning. Conditions such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge‑eating disorder and other specified feeding or eating disorders fall into this category.

Image: Google
Evidence from Nigerian research confirms that disordered eating attitudes and risk for eating disorders are present among young adults and adolescents. In a study of more than 1,050 undergraduates from two higher‑education institutions in Lagos, roughly 16 percent scored positive on the EAT‑26 screening tool for disordered eating attitudes.
At a university in Ile‑Ife, a survey of female undergraduates found that 17.1 percent were classified as at high risk for eating disorders, based on the same screening instrument.
A more recent analysis among female undergraduates in Lagos found a lower prevalence of disordered eating (about 5 percent). Still, the study flagged a strong association between body-image dissatisfaction, body‑mass index (BMI) and disordered eating attitudes.
Adolescents are not exempt: a survey of 13 to 19-year-olds in Ibadan used screening tools to assess disordered eating behaviours and feeding/eating disorders. Results showed that 28.2 percent exhibited disordered eating behaviours, and a significant portion also met screening criteria for feeding/eating disorders.

Image credit: Google
Clinical, clearly diagnosed cases have also been documented. There’s a recorded instance of a 20-year-old undergraduate at a Nigerian university diagnosed with anorexia nervosa showing that what may start as dieting or food anxiety can escalate into serious health and psychiatric risk.
Because disordered eating and eating disorders exist within the Nigerian context, distinguishing between them matters. Persistent preoccupation with food, weight or body shape; regular dieting, bingeing or purging; emotional distress tied to eating; and disruption of everyday life are all red flags. When those signs persist, seeking professional support whether nutritional counselling, psychological therapy or medical care becomes essential.
Health
The Exercise That Keeps You Younger
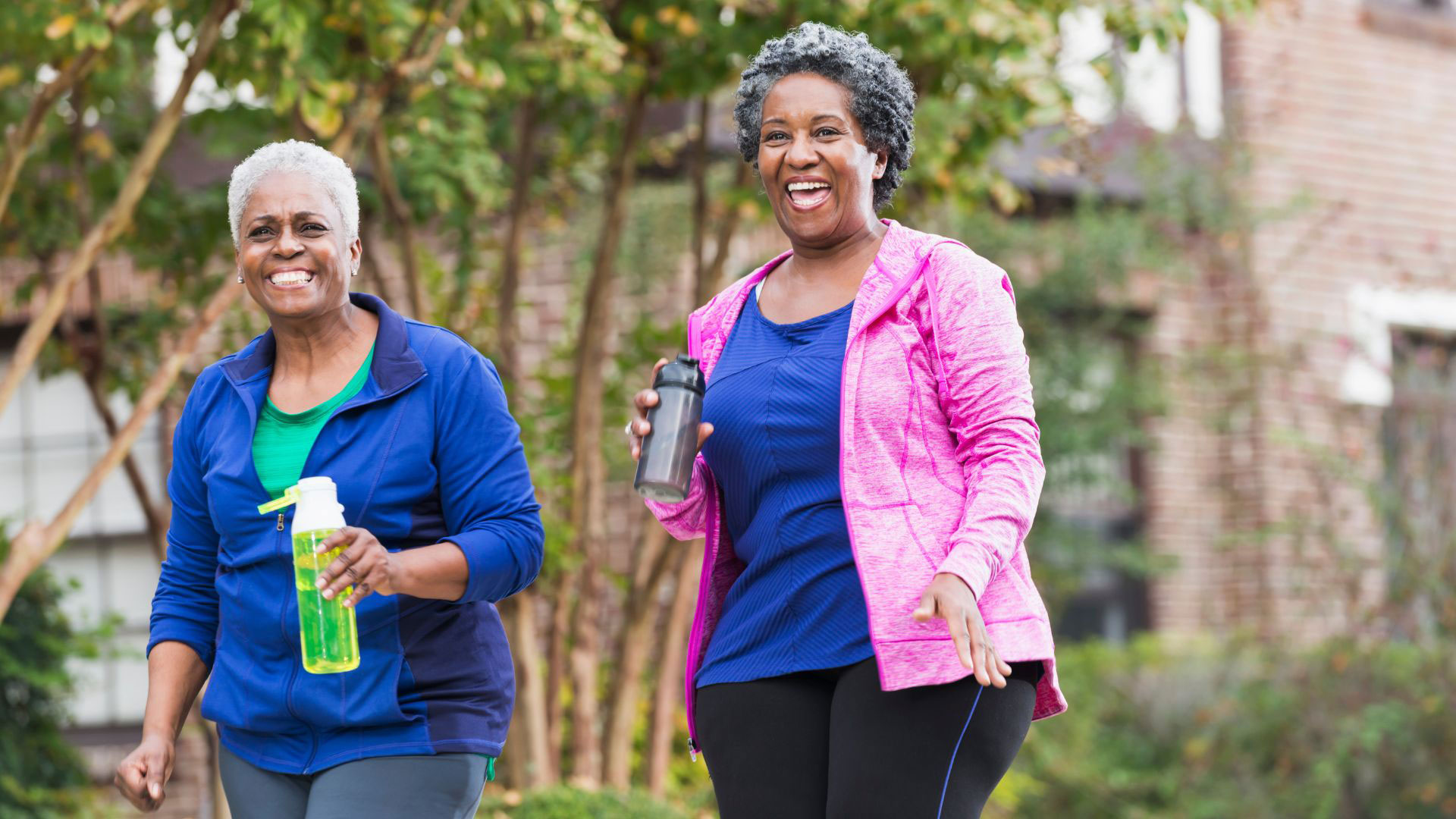

If you’ve ever met someone in their fifties who moves like they’re still in their twenties, it’s likely they’ve discovered the simple habit that keeps the body from giving in to age: regular movement.

While fitness trends keep changing, one form of exercise has stayed constant in its benefits: strength training. It’s not about building bulky muscles or chasing a perfect body. It’s about keeping your bones strong, your joints stable, and your metabolism from slowing down. After the age of 30, the body naturally begins to lose muscle each year. That’s why everyday tasks, like climbing stairs or carrying groceries, start to feel heavier. Strength training helps reverse that.

Research supports this claim. People who lift weights or engage in resistance exercises have lower risks of diabetes, heart disease, and cognitive decline. But beyond the science, it’s about how it makes you feel. Nigerians juggling work, traffic, and family life know how draining each day can be. Even short sessions of body-weight squats, lunges, or push-ups a few times a week can recharge you better than most expensive wellness fads.

It also boosts your mood. Physical activity releases chemicals that help clear mental fog and lift your energy. It’s your body’s way of proving it still has strength to give.
You don’t need a gym to start. A mat, a pair of dumbbells, or even two water bottles will do. The goal is to stay consistent, to keep your body active enough to stay responsive.
Each push, lift, or stretch is a reminder that staying young isn’t about denying age; it’s about moving through it with strength.
-

 Celebrity Style5 months ago
Celebrity Style5 months agoMercy Aigbe Keeps it Sharp in Ivory Dress
-

 Celebrity Style5 months ago
Celebrity Style5 months agoBella Okagbue Puts a Spin on Feminine Suiting
-

 Fashion5 months ago
Fashion5 months agoTeminikan Experiments with Geometry in a Woven Mini
-

 Lagos Fashion Week4 months ago
Lagos Fashion Week4 months agoLagos Fashion Week’s Earthshot Prize Win Highlights a Changing Direction in African Fashion Production
-

 Celebrity Style4 months ago
Celebrity Style4 months agoDiadem Okojie Perfects Polka Dots
-

 Celebrity News4 months ago
Celebrity News4 months agoBurna Boy Commands the Spirit Tunnel on The Jennifer Hudson Show
-

 Top Xclusiv4 months ago
Top Xclusiv4 months agoAnok Yai Named Model of the Year 2025 at the Fashion Awards
-

 Celebrity Style2 months ago
Celebrity Style2 months agoPantone’s 2026 Colour Cloud Trend Gets Uche Montana’s Seal of Approval
-

 Movies4 months ago
Movies4 months agoTrailer Review for “Safari”
-

 Celebrity Style3 months ago
Celebrity Style3 months agoChioma Ikokwu Wears Lanre DaSilva Ajayi’s SS26 Couture at the Designer’s 20-Year Celebration






















